Everything you need to know about AMD’s 3rd Gen/Zen 3 EPYC processors
Everything you need to know about AMD’s 3rd Gen/Zen 3 EPYC processors
Thanks to their Zen 3 architecture and a revamped I/O die, AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors can deliver large leaps in raw performance, tighten their security mechanisms and provide their customers with increased versatility. AMD’s 3rd Generation is more than a mere Zen 3 refresh of 2nd Gen EPYC; it is an upgrade that pushes AMD forward on almost all fronts.Â
Over the next few pages, we will be discussing AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors in detail. Get ready to meet the EPYC 7003 series.Â
Taking jabs at Intel
Let’s face it; Intel’s execution within the data centre market has been poor for several years. Intel has been stuck on 14nm for too long, and Intel’s Skylake and Cascade Lake architectures are in dire need of replacement.Â
In February 2020, Intel released “performance-per-dollar-optimized processors” onto its Xeon Scalable product line, thinly veiled price cuts to counter AMD’s 2nd Generation EPYC lineup. Intel’s next-generation Ice Lake enterprise lineup has been delayed time and time again, and now AMD has new Zen 3-based EPYC processors to compete with Cascade Lake.Â
AMD’s pre-briefing on 3rd Generation EPYC discusses AMD’s “Predictable Execution” and the fact that AMD is “making good on our promises”. Intel’s enterprise delays have hit their reputation hard, and AMD is more than willing to take advantage of that.Â
Intel’s ageing Cascade Lake lineup is also granting AMD a huge performance lead. Ice Lake is not available yet, which means that AMD’s Zen 3 enterprise lineup is still being compared to Cascade Lake, and these comparisons are not doing Intel any favours. Intel’s inability to execute is handing AMD free market share.Â
Â
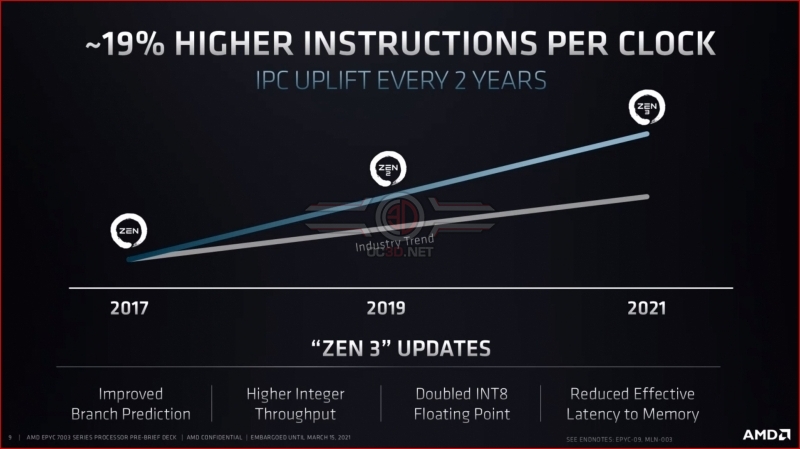
If you have read our Ryzen 5000 series reviews, you will know that Zen 3 is a great CPU architecture. With EPYC, AMD promises the same 19% IPC uplift over Zen 2, delivering 3rd Generation EPYC users a solid uplift in system performance.Â
AMD’s 19% IPC uplift is a geomean from various workloads, which means that Zen 3 can deliver larger and smaller performance boosts depending on your specific workload. Even so, a 19% average is an excellent improvement, so much so that Zen 3 deliver AMD’s highest generation-to-generation IPC uplift for their Zen family of processors.
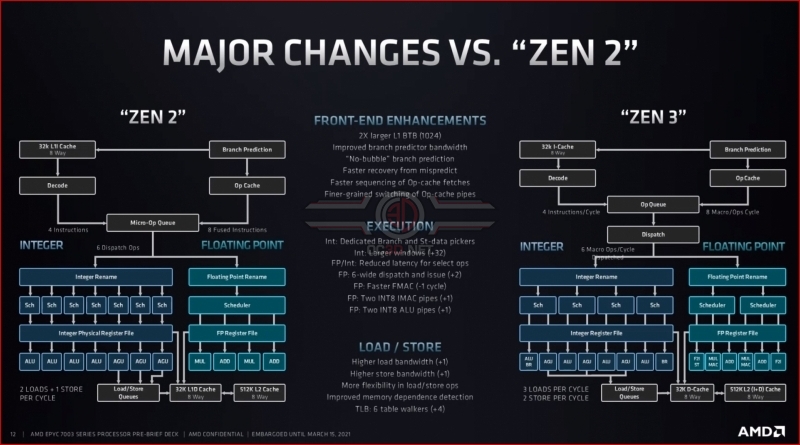
With Zen 3, AMD’s EPYC lineup boasts doubled INT8 performance for inferencing workloads, improved integer performance, improved branch prediction and reduced effective memory latencies. These enhancements can be transformative for specific workloads and make 3rd Generation EPYC processors a compelling upgrade for certain enterprise users.Â
 Â Â
 Â
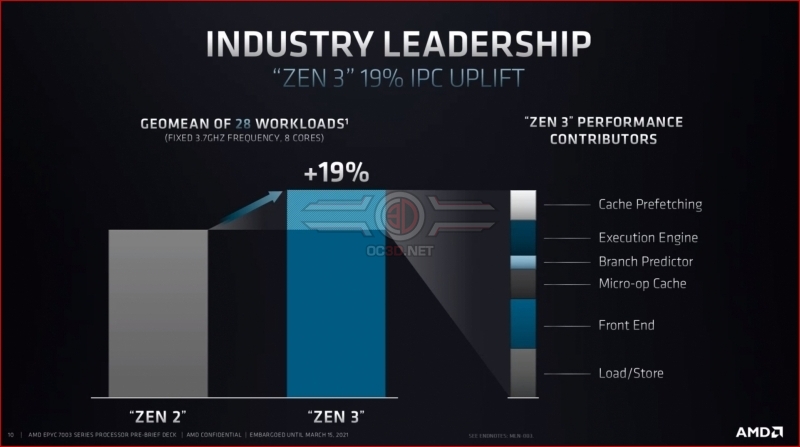
AMD’s Zen 3 architecture makes improvements across its core architecture. No single change is responsible for AMD’s 19% IPC boost. With Zen 3, many small improvements have added up to create a large overall IPC improvement. This allows Zen 3 to deliver boosted performance across a wide range of workloads and for these performance improvements to be substantial in many cases.Â
 Â Â
 Â
The slide below goes into some of the nitty-gritty details of Zen 3, but the shorthand is that AMD has made its branch prediction less latent, more accurate, and better at handling its mistakes, the core’s L1 cache has been doubled in size, the core’s load/store functionality has been made more flexible/less fixed function, and several sections of its execution pathways have been widened.Â
 Â Â
 Â
What’s new with 3rd Gen EPYC
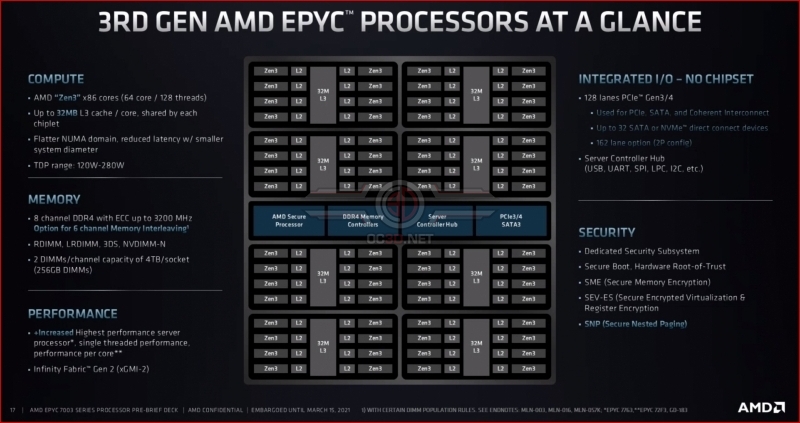
As we mentioned before, AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors offer more than simple Zen 3 performance enhancements. AMD has confirmed to us that 3rd Generation EOYC processors also include a revamped I/O die.Â
This new I/O die adds new features to AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors, tightens AMD’s processor security and adds 6-channel memory support to the processor. This makes 3rd Generation EPYC processors more versatile while retaining drop-in compatibility with EPYC 7002 (2nd Gen) systems.Â
 Â Â
 Â
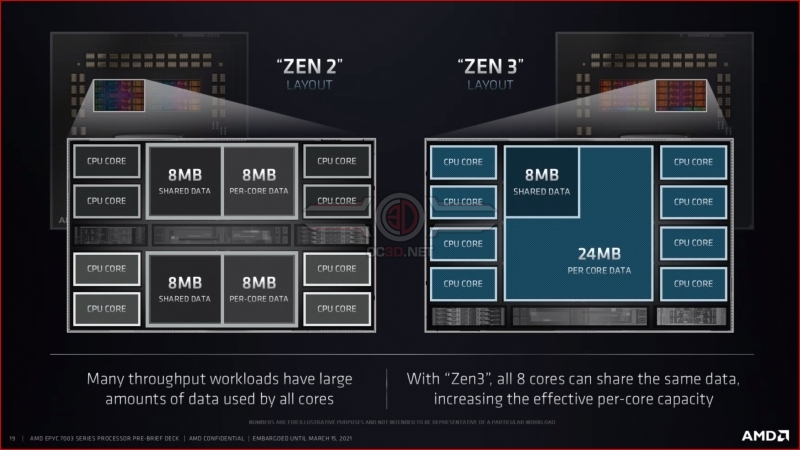
Zen 3’s enhanced cache structure is EPYC!
With Zen 1 and Zen 2 series processors, each 8-core CPU chiplet is constructed with two 4-core CPU complexes. These two CPU complexes contain separate L3 caches, and communications between these CPU core clusters and caches feature a severe latency penalty.Â
With Zen 2, these core complexes featured 16MB of cache each, offering 32MB of combined cache across the 8-core CPU die. One of Zen 3’s major innovation is the architecture’s use of 8-core CPU complexes, making the eight CPU cores within a Zen 3 CPU die a singular core cluster with a single combined L3 cache.Â
With Zen 3, all eight cores can communicate without a latency penalty, and each core now has access to a combined 32MB pool of L3 cache. This allows for faster core-to-core communications within a single CPU core complex (CCX), while giving each core access to more L3 cache.Â
Zen 3 can more than double effective per-core cache capacity!
While Zen 3 allows cores to access 2x as much L3 cache, the reality is that AMD has managed an even more impressive feat. With a single combined L3 cache, each CPU die no longer needs to dedicate parts of each separate L3 cache to the same data. With Zen 3’s combined cache structure, AMD can more than double each core’s cache access by eliminating the need for duplicate data.Â
 Â Â
 Â
Please load onto the next page
New Features – Security, Memory and ISA enhancements
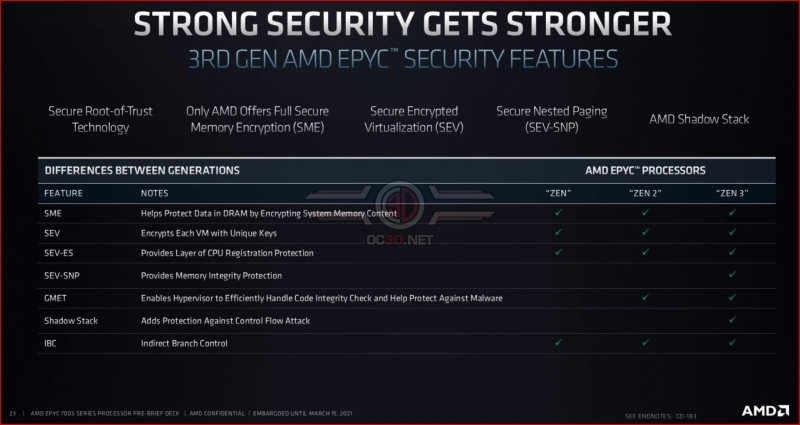
With their 3rd Generation EPYC processors, AMD has revamped their processor’s I/O die to enable new security features. With these changes, AMD has made their processors more secure and has added additional value to their EPYC processor line. 3rd Generation EPYC is about more than performance; it’s about all aspects of customer value.Â
 Â
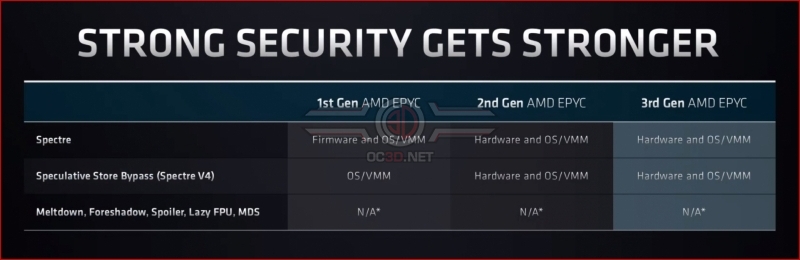
In their pre-briefing, AMD discussed the ongoing impact of Spectre and similar side-channel attacks. With 2nd Generation and 3rd Generation EPYC, AMD has hardened the security of their processors, with 3rd Generation EPYC receiving stronger hardware-based security improvements.Â
The chart below highlights a lot of speculative execution attacks, most of which are not applicable to AMD’s processors. This is yet another jab at Intel and the frequency of speculative execution attack discoveries for Intel-based CPU platforms. In this regard, AMD is painting a clear picture; that their processors are more secure than their rivals.Â
 Â Â
 Â
With their EPYC 7003 series, AMD’s made their product line more versatile, as they know that their customers will want to do everything that they can to deliver more value within their systems.Â
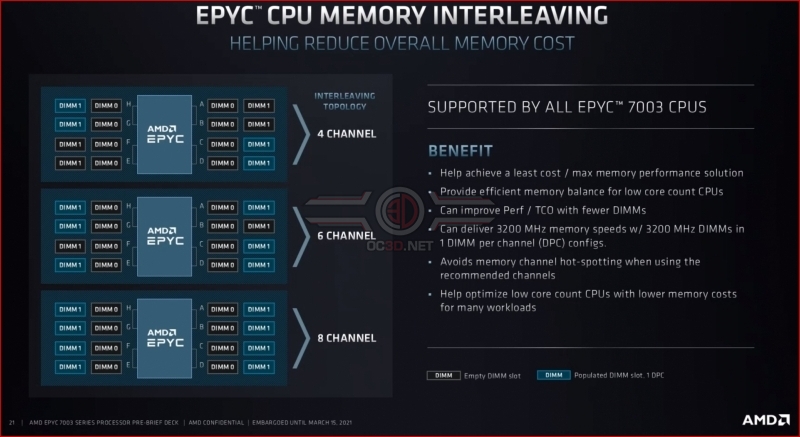
With EPYC 7003 processors, AMD has upgraded their I/O die to handle 6-channel memory configurations better and deliver better performance on systems that use fewer memory DIMMs. This is great news for EPYC users who don’t need the bandwidth or high memory cappacities 8-channel memory configurations. This change gives system integrators more options, and that’s good for AMD’s bottom line. Â
 Â Â
 Â
With their EPYC 7003 processors, AMD has also added some new ISA instructions to enhance the security and performance of their processors. These features enable a higher level of system optimisation for EPYC processors, which is good for AMD in the long-term.Â
 Â Â
 Â
In all, AMD’s 3rd generation 7003 EPYC processors deliver more computational performance, more versatile configuration options and compatibility with both new and existing server designs.Â
Users of 2nd generation EPYC servers will only need a BIOS update to support 3rd Generation EPYC processors, which will come as great news for customers who wish to upgrade to AMD’s latest wares.Â
Performance and Pricing – EPYC extends its lead
As we have said before, Intel’s inability to execute has allowed AMD to build up a significant lead across a wide range of applications. Within Cascade Lake’s lifespan, AMD has launched their 2nd Generation and 3rd Generation EPYC processors.Â
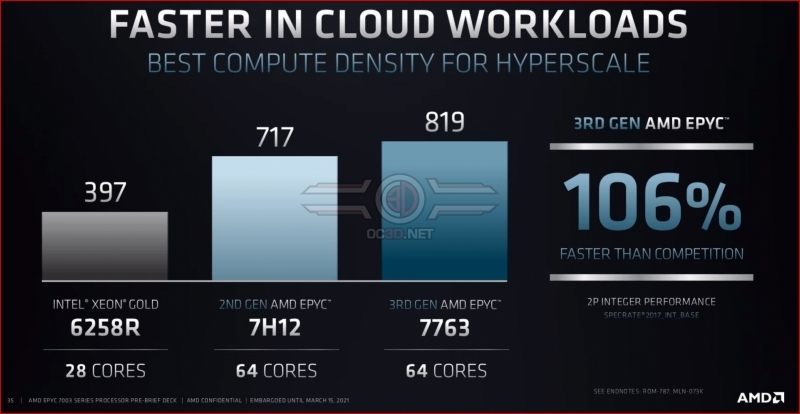
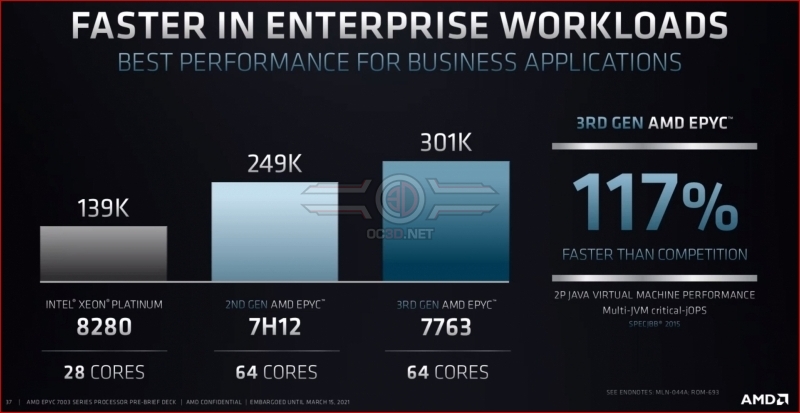
With their Zen 2 (7002 series) EPYC processors, AMD already put up a good fight against Intel. With Zen 3, AMD makes a mockery of Intel’s single-socket performance. Across Enterprise, Cloud and HPC workloads, AMD claims a 2X performance improvement with their top EPYC processor.Â
 Â
 Â Â
 Â
The Versatility of Zen 3 EPYC
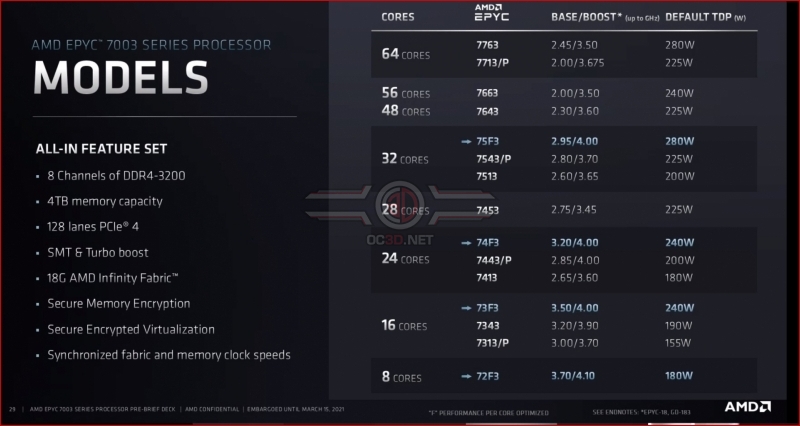
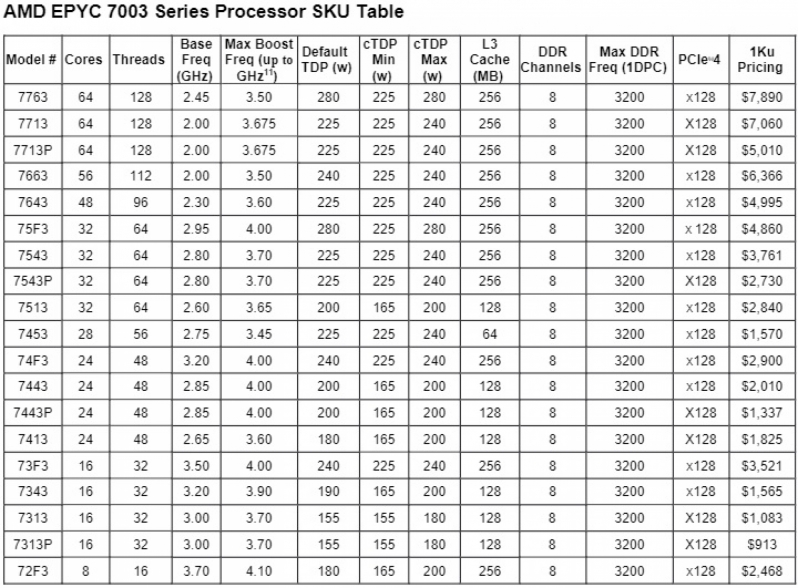
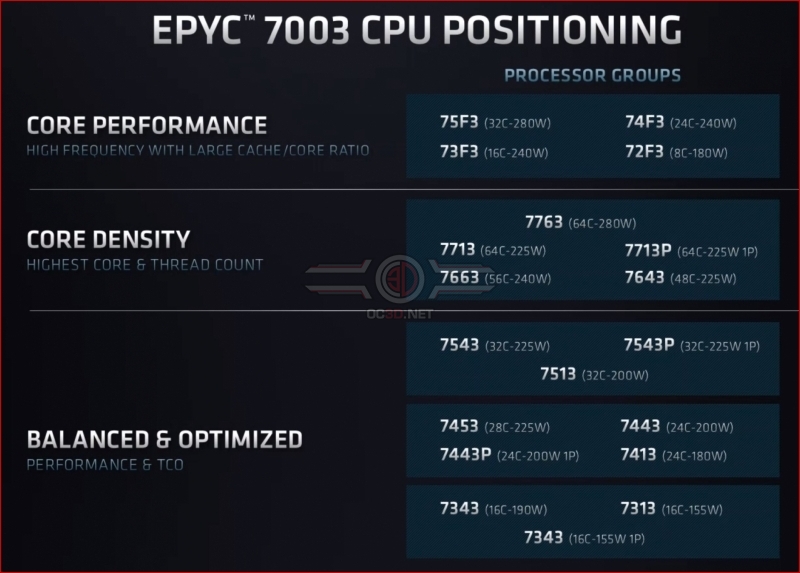
AMD’s EPYC 7003 series offers users a wide range of processor configurations, offering server providers 8-core, 16-core, 24-core, 28-core, 32-core, 48-core, 56-core and 64-core product options. Better still, all of these CPU options have the same I/O capabilities, support for 8-channel memory, support for up to 4TB of DRAM, 128 PCIe 4.0 lanes and the same security features.Â
AMD’s lineup is also split into options that can vary when it comes to L3 cache per core and characteristics like CPU TDPs and clock speeds.Â
AMD’s EPYC 7003 series of processors features models tweaked to deliver higher levels of core performance, core density or value for money. Some models feature disabled cores and larger L3 caches to deliver peak levels of single-threaded performance. In contrast, others are designed to enable the highest core counts or deliver more value for money.Â
AMD’s 7003 series of EPYC processors will provide users with plenty of configuration options, offering more variety than simple core count and clock speed alterations.Â
 Â Â
 Â
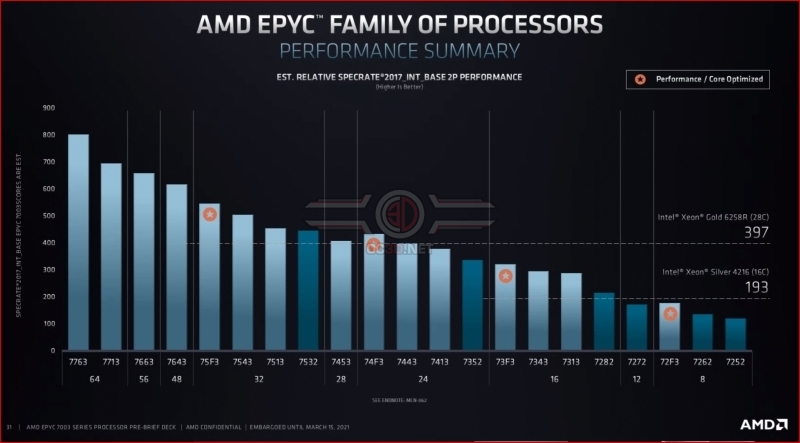
Compared to their last-generation counterparts, AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors deliver a significant performance improvement over their predecessors and their Intel-based rivals. This should help AMD to attract new customers, assuming that AMD has the manufacturing capacity to supply them.Â
 Â Â
 Â
Below are some charts comparing Intel’s current single socket XEON Scalable flagship with AMD’s top-end 3rd Generation EPYC processor across HPC, Cloud and Enterprise workloads. AMD has claimed performance leadership in all areas, though it is worth remembering that AMD has supplied its own data.Â
Â
Below is a list of all of AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC SKUs, complete with US pricing and cache configuration data.Â
Â
Â
Conclusion – EPYC gets more EPIC!
AMD’s 7003 series of 3rd Generation EPYC processors delivers on the potential of Zen 3, delivering the same innovations as the Ryzen 5000 series while also endeavouring to provide their enterprise customers with more versatility and tighter security.Â
With a 19% IPC increase, AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors don’t require more cores or threads to compete with their Intel counterparts. With Zen 3, AMD has extended its leadership within the enterprise market, further strengthening its already robust 2nd Generation EPYC offerings with increased performance and new platform features.Â
AMD has managed to keep its promises with their EPYC processor roadmap, making a mockery of Intel’s frequent processor delays and the long-lived nature of the Cascade Lake product line. AMD is delivering strong generational gains in performance while Intel has stagnated, and Intel needs to respond to this.Â
 Â
With their Zen 3 cores, AMD has given their processor cores access to more L3 cache and a wide range of architectural improvements, delivering performance improvements across practically all workloads without increasing their power consumption over their last-generation EPYC CPUs.Â
AMD’s EPYC 7003 processors deliver solid pricing, excellent performance and more versatility to their customers. In short, AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors are a clear win for the company. The only problem that we foresee for EPYC is availability, as these processors are going to sell like hotcakes.Â
You can join the discussion on AMD’s 3rd Generation EPYC processors on the OC3D Forums.Â