Micron reveals the future of GDDR7 memory
GDDR7 will make it easier to give GPUs tonnes of VRAM
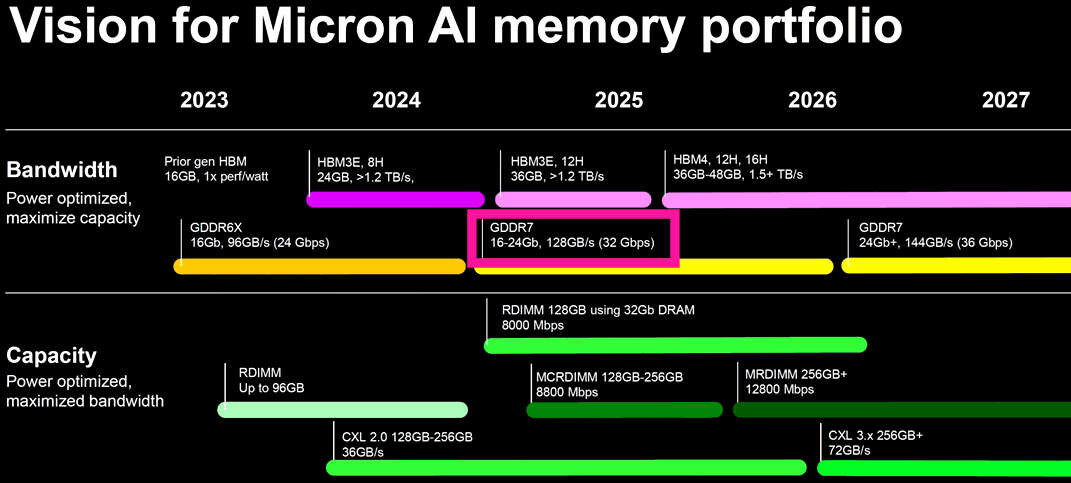
This week, JEDEC published their official GDDR7 memory standard, ushering a new era of GPU memory performance. Now, thanks to 3DCenter.org, we have received a look at Micron’s memory roadmap, revealing their plans for GDDR7.
One of the most interesting aspects of GDDR7 isn’t its raw bandwidth, it’s the memory’s planned capacities. 16Gb (2GB), 24Gb (3GB), 32Gb (4GB), 48GB (6GB), and 64GB (8GB) modules are part of the GDDR7 standard. Within their roadmap, Micron has clear plans to create 24Gb and larger GDDR7 modules. This has interesting ramifications for future graphics cards.
Larger frame buffers on smaller memory interfaces
Today’s GDDR6 and GDDR6X memory modules top out at 16Gb (2GB) chip sizes. With larger 3GB chips, GPU manufacturers will be able to create GPUs with larger VRAM capacities on smaller memory busses. For example, today’s 2GB GDDR6 chips can he used with a 128-bit memory bus to create 8GB graphics cards using four memory chips. With GDDR7 and 3GB chips, a 128-bit memory bus can be used to create 12GB GPUs.
With larger GDDR7 chip capacities, it will be easier for GPU manufacturers to create graphics cards with larger frame buffers. While it is possible today to create 16GB GPUs using a 128-bit memory bus by using eight 2GB memory chips in clamshell mode, this is a costly process. With larger GDDR7 chips, GPUs with large frame buffers will be much easier to produce. That said, it will take a while before we see 4GB, 6GB, or larger GDDR7 chips.
| 16 Gbit / 2 GB per chip | 24 Gbit / 3 GB per chip | 32 Gbit / 4 GB per chip | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 128-bit interface (= 4 memory chips) | 8GB VRAM | 12GB VRAM | 16GB VRAM |
| 192-bit interface (= 6 memory chips) | 12GB VRAM | 18GB VRAM | 24GB VRAM |
| 256-bit interface (= 8 memory chips) | 16GB VRAM | 24GB VRAM | 32GB VRAM |
| 384-bit interface (= 12 memory chips) | 24GB VRAM | 36GB VRAM | 48GB VRAM |
Micron plans to make faster and more storage dense GDDR7 modules
Micron’s roadmap highlights plans to create 16Gb and 24Gb memory chips this year. These modules will offer users speeds of 32 Gbps. That’s 60% more memory bandwidth than the 20Gbps GDDR6 chips used on AMD’s RX 7900 XTX.
AMD’s Radeon RX 8000 series GPUs and Nvidia’s RTX 50 series graphics cards are both likely to feature GDDR7 memory. Both architectures are due to launch before the end of this year.
You can join the discussion on Micron’s GDDR7 memory plans on the OC3D Forums.