ATX12VO Tested – The Future of Power Supplies?
ATX12VO – A Drive for Efficient Computing
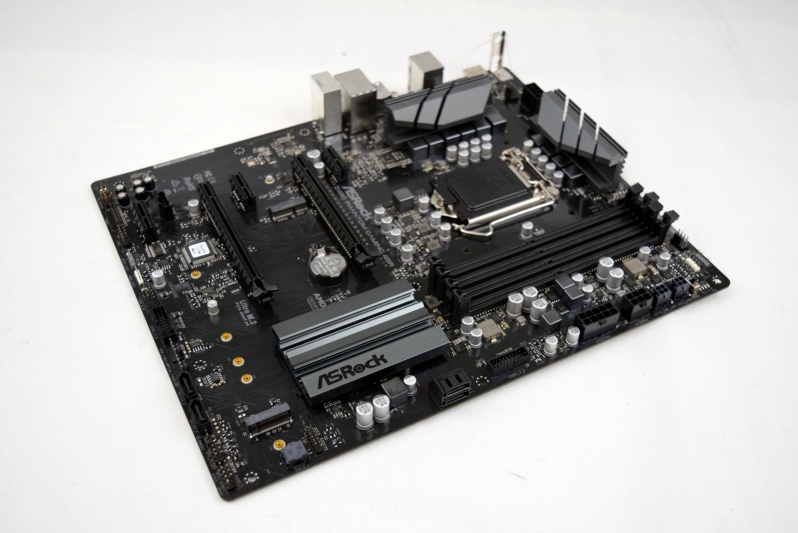
Last year, Intel and ASRock teamed up to create the world’s first ATX12VO motherboard, adopting a new standard which has the potential to change computing forever.
At this point, it cannot be denied that global warming is a thing. Because of that, the world has increased its focus on energy efficiency, be it for heating your home, public/personal transport and the electrical efficiency of our appliances and computational devices. That’s where ATX12VO comes in.
In 2019, Intel released its ATX12VO standard, and it is designed to decrease the idle power usage of future PCs. This article will look at how this new power standard works and why it focuses on idle power consumption. Beyond that, we will also be looking at the downsides of this standard, and what will hamper its adoption within the consumer PC market.
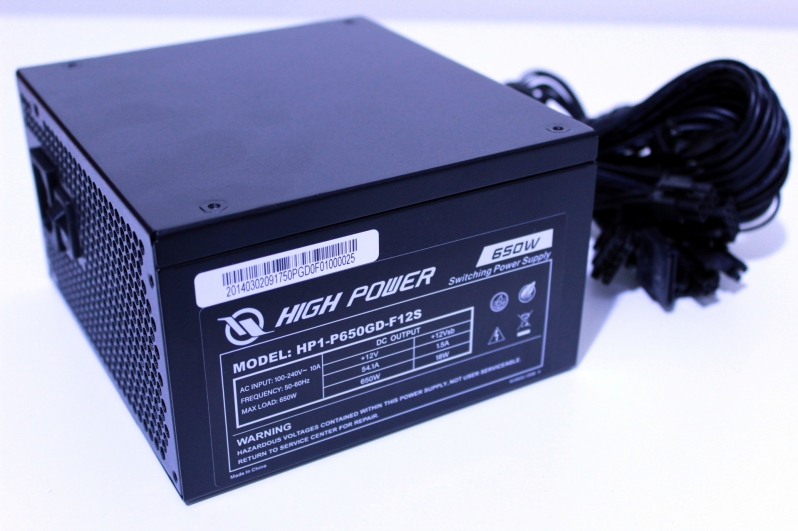
Intel has supplied us with an ASRock Phantom Gaming 4SR motherboard, an i9-10850K, and a High Power HP1-P650GD-F12S power supply to test their ATX12VO technology. These components are what will allow us to compare components using ATX12VO power with conventional PC components. To be clear, Intel has no editorial control over this article and has no say on our testing methods. They supplied the parts, and from there, we tested.
What is ATX12VO?
The simple way to think of ATX12VO is to say that it is an ATX power supply standard that only features a 12V rail. That’s why it is ATX12VO; it’s ATX 12 Volt Only!
Standard ATX power supplies utilise multiple rails to deliver its power, offering users 5V and 3.3V rails in addition to their 12V rail. While many PC parts only need 12V power, others require these lower voltages to function correctly, which means that power supplies need to do multiple voltage conversions at variable loads.
The complexity of traditional power supplies makes multi-rail power supplies inefficient at lower wattages, which means that your PC is most inefficient when it is at idle and other low power states. Most desktop PCs are used for light tasks like internet browsing and video playback, making all of those low wattage inefficiencies add up to create a lot of wasted electricity, especially on a global scale.
ATX12VO power supplies increase the efficiency of low power draw scenarios by using a single 12V rail exclusively. This design also makes ATX12VO power supplies less expensive to produce, as only one voltage conversion is necessary. 5V and 3.3V conversion will take place on the motherboard for the components that need it, so some of these decreased PSU manufacturing costs will be transferred over to higher motherboard costs. Even so, ATX12VO systems promise to deliver higher efficiency levels at low wattage workloads.
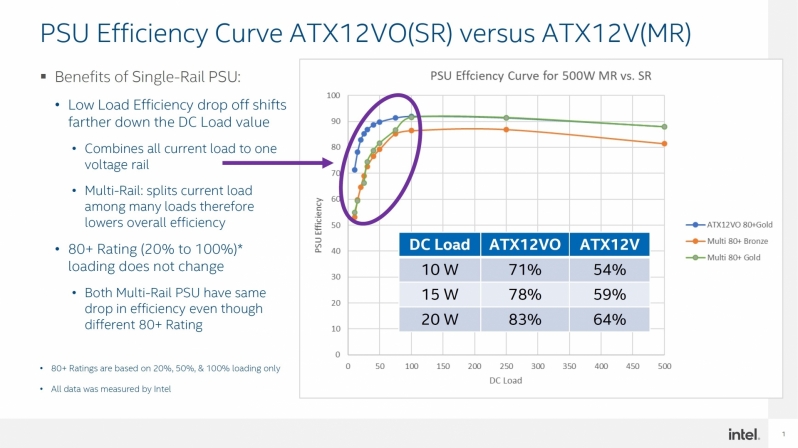
When PSU load increases, the efficiency of standard PSUs reach their peak, making ATX12VO PSUs no more efficient than traditional PSU designs. That said, most systems do not stay at 50-100% loads under most situations, assuming that your system isn’t exclusively used for rendering or gaming. The graph below showcases the power efficiency of ATX12VO PSUs when compared to ATX PSUs.
Who is ATX12VO For?
Ideally, Intel’s ATX12VO standard is for everyone, but for now the standard of most interest to OEM PC builders, especially those who live in countries which are actively legislating the desktop PC industry. New regulations mandate higher efficiency levels for desktop computers, and ATX12VO will help these PC makers comply with these regulations.
Some PC manufacturers were already using a similar 12V only standard for their OEM systems, but the ATX12VO standard will allow them to start working from the same spec sheet. This will allow PSU makers to create PSUs that use fewer proprietary connections and standardise 12V only PSU/system setups. This will help make 12V only power systems cheaper to implement and easier to adopt by other manufacturers.
DIY PCs will not need to follow these new power efficiency standards, making ATX12VO power systems a harder sell for the custom PC market. New power supplies with new connectors would require PC builders to purchase a new PSU and motherboard to adopt the standard, and that will not be welcome news to anyone who has recently purchased a new high wattage power supply.
While ATX12VO 10-pin adaptors can be made for today’s ATX12V power supplies, such adaptors require PSU makers to be willing to support ATX12VO and allow users of their existing units to transition to the standard without purchasing new PSUs. As of now, Corsair is the only manufacturer that has created an ATX12VO adapter for their existing power supplies.
In the following pages, we will discuss the downsides of the ATX12VO standard, its advantages and how it impacts power consumption using real-world wattage measurements. Use the links below to navigate to your desired page quickly.
Contents
– Introduction – What is ATX 12VO
– Complications – New connectors, SATA power and other voltages
– Testing – Are ATX 12VO PCs much more efficient?
– Conclusion – Is ATX12VO the future?