AMD Raven Ridge Ryzen 3 2200G and Ryzen 5 2400G Review
Test Setup and Architectural changes
AMD’s Raven Ridge CPU design sits at a midway point between AMD’s existing Summit Ridge series of Ryzen processors and their upcoming “Ryzen +” series of CPUs, with the latter being set for a release in April.Â
This places Raven Ridge in a strange position, coming with the same basic CPU design as AMD’s existing Ryzen processors on the same 14nm process from GlobalFoundries while benefitting from some of the improvements that are coming to Ryzen+. The most notable of these changes is the inclusion of Precision Boost 2 and alterations to cache latencies.Â
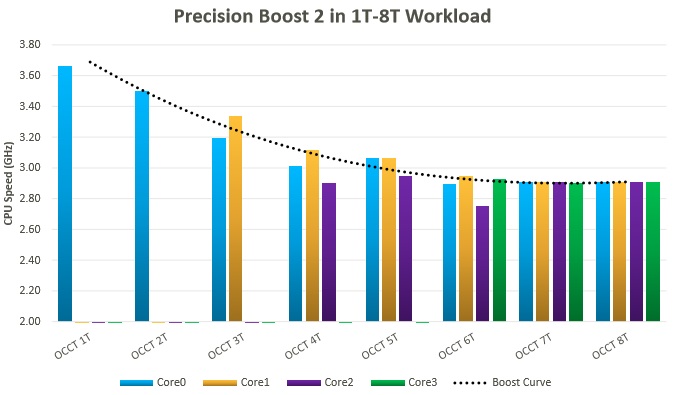
Precision Boost 2 is the name of AMD’s latest boost algorithm which specifies what clock speed a product should be running at under specific workloads, improving upon the implementation that AMD delivered with their 1st generation Ryzen designs.Â
With Ryzen AMD’s boost clock technology was notably behind Intel’s, offering fewer intermediary points for optimal core boosting. With Ryzen there were not many intermediary stages for boost clocks, giving an almost all or nothing approach to core boost clocks, leaving a lot of Ryzen’s potential untapped.Â
The graph above illustrated AMD’s boost behaviour with Precision Boost 2, showcasing varying boost clocks as workloads start to use more CPU cores. This change allows AMD to offer higher CPU clock speeds in lightly threaded workloads, accelerating general computing applications.Â
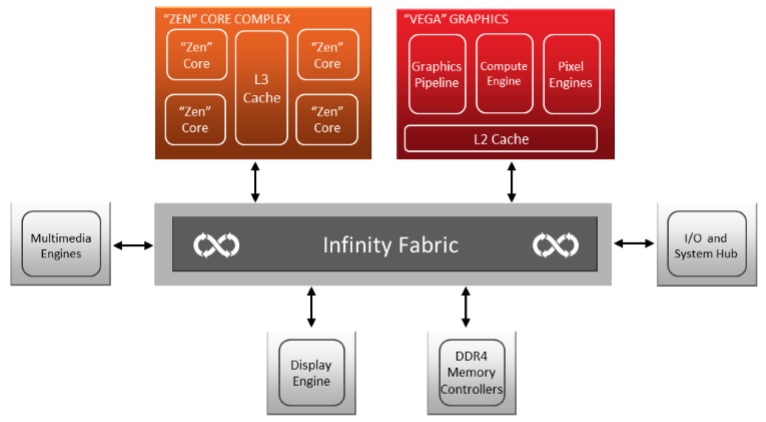
Raven Ridge is also designed to make better use of AMD’s Infinity Fabric technology, allowing a Ryzen CPU module to be integrated with a Vega graphics component, giving both access to the products I/O and memory subsystems. Vega is the first AMD GPU architecture to utilise Infinity Fabric, with an APU acting as the perfect place to showcase this new functionality, especially when given an APU’s required low power requirements.Â
Vega is a much more power efficient architecture at lower clock speeds, making Raven Ridge the fastest APU to date in terms of GPU clock speed, while also offering an increased maximum GPU core/stream processor count. Combine this with Vega’s other architectural enhancements and AMD has a compelling offering on their hands.Â
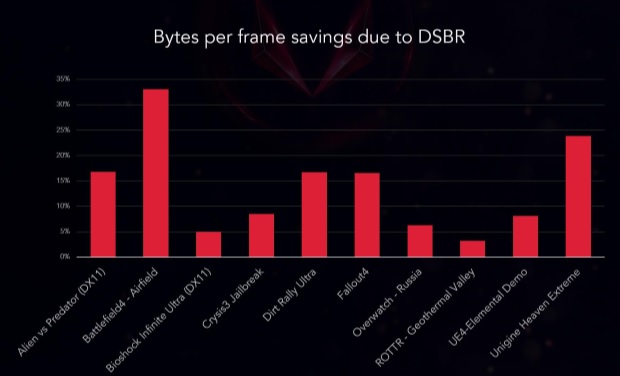
While all of Vega’s architectural advancements are worth mentioning, the most noteworthy of them is AMD’s new Draw-Steam-Binning-Rasteriser. This is a technique that AMD can use to reduce the number of bytes per frame that are required while rendering, decreasing the memory bandwidth that is required by the processor.Â
This change is huge for an APU, as their reliance on DDR system memory has traditionally head back their game performance. Combine this with the move to higher bandwidth DDR4 with Raven Ridge and we should see memory speed have an overall lower impact on GPU performance, at least when compared to older APUs.Â
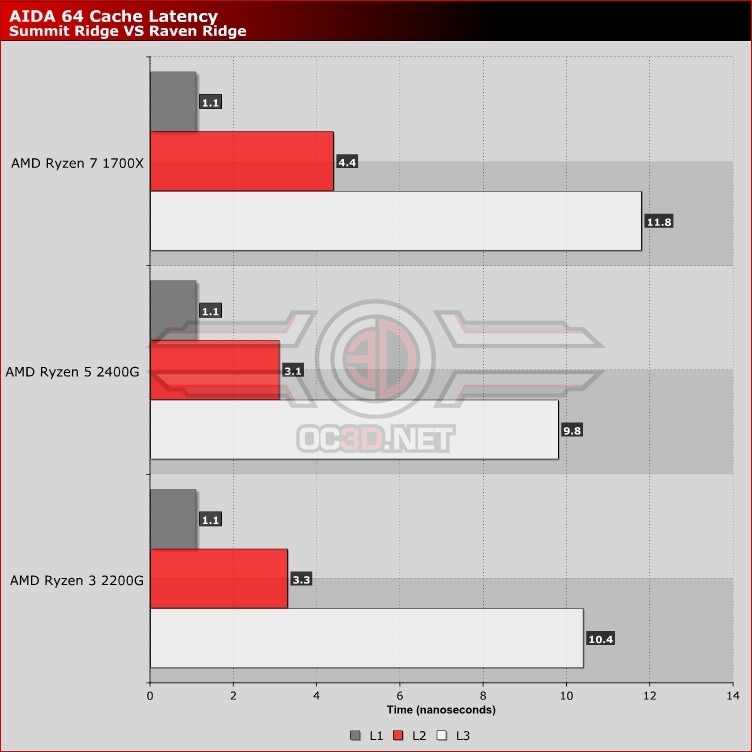
One of the many changes that AMD has noted with their Raven Ridge series CPUs is a reduction in cache latencies, something that many of Ryzen’s critics have been crying out for, particularly within the game emulation scene.Â
AMD has noted that they improved their cache latencies in Raven Ridge, though we were not satisfied with AMD’s word here and decided to confirm this for ourselves using AIDA 64’s Cache latency and bandwidth test, where we found some significant changes.Â
While L1 cache latencies remain similar, both L2 and L3 cache latencies are significantly reduced, with a decrease of around 25% when moving our 1700X to AMD’s new Raven Ridge processors on the products L2 cache and a reduction of approximately 9% on the product’s L3 cache. This improvement allows Raven Ridge to react faster on cache-sensitive workloads, with these improvements being expected to carry on to AMD’s upcoming Ryzen + CPU designs later this year. Â
Â
Test Setup
AMD Ryzen 3 2200G & Ryzen 5 2400G
ASUS Prime B350-PLUS
G.Skill Flare X 3200MHz memory
Corsair RM1000i
Corsair MP500 512GB
Corsair H110i GT
Windows 10
Â